WHY TURKEY ?
10 Reasons to Study in Turkey
1. QUALITY HIGHER EDUCATION OPPORTUNITIES
Turkey is the second country in the world in access to higher education with 94.2% schooling rate. Turkey involved in European Higher Education Area is implementing the Bologna Process in a perfect way; our Bologna report is 5 out of 5. So, the diploma you receive from a university in Turkey is recognized in all European countries! As course credit system, ECTS is applied in accordance with Europe and all students are given Diploma Supplement. In addition, Turkey is one of the most successful countries participating in the exchange programs under Erasmus +. In addition to Erasmus, there are many exchange programs in Turkey, such as Mevlana, Farabi, which support the mobility of students and lecturers.
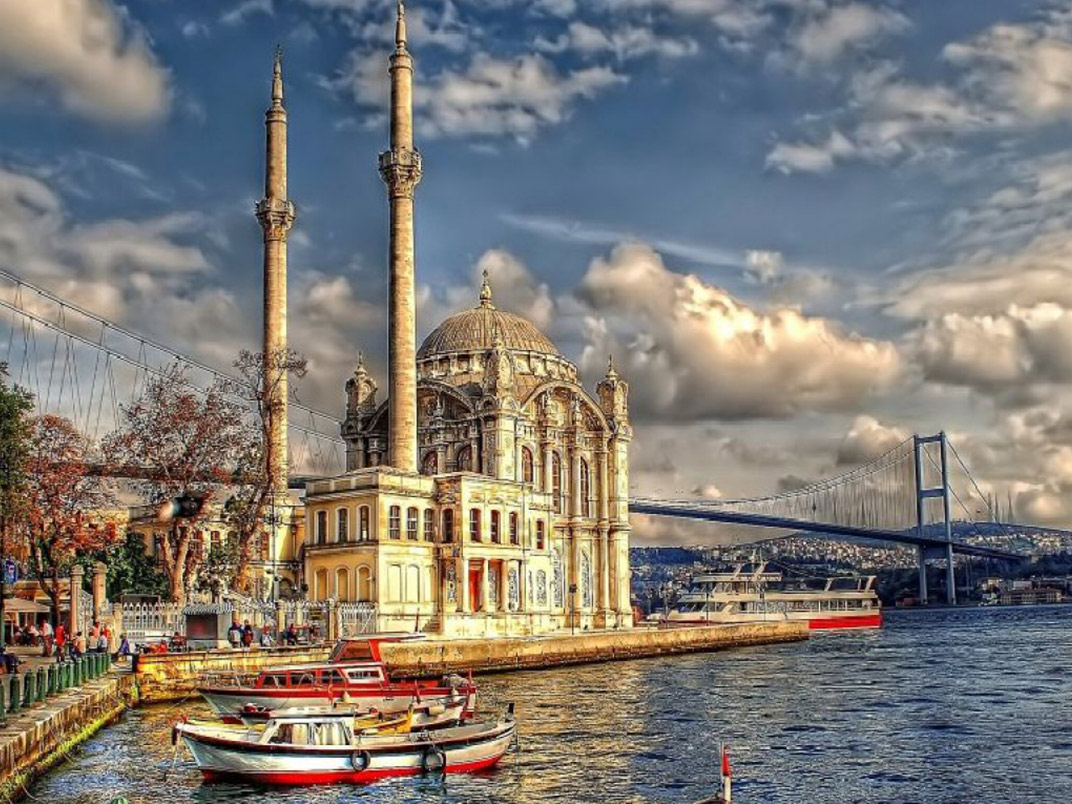

2. University And Program Diversity
There are 206 universities in Turkey with a population of 82 Million. The number of students is close to 8 million. With this number of students, Turkey is the first country with the most students in European Higher Education Area. There are a total of 58,092 different programs at 206 universities. In such a variety, you will definitely find a university and program for yourself.
3. Multicultural Life
Turkey, which has hosted many deep-rooted civilizations in its territory for thousands of years, is almost a mosaic of cultures! In this country where countless civilizations have been hosted, everyone is tolerant and respectful to each other. Turkey, where you can find a piece of your roots and perhaps can meet people who speak your language is ideal for students with its safe and peaceful environment.
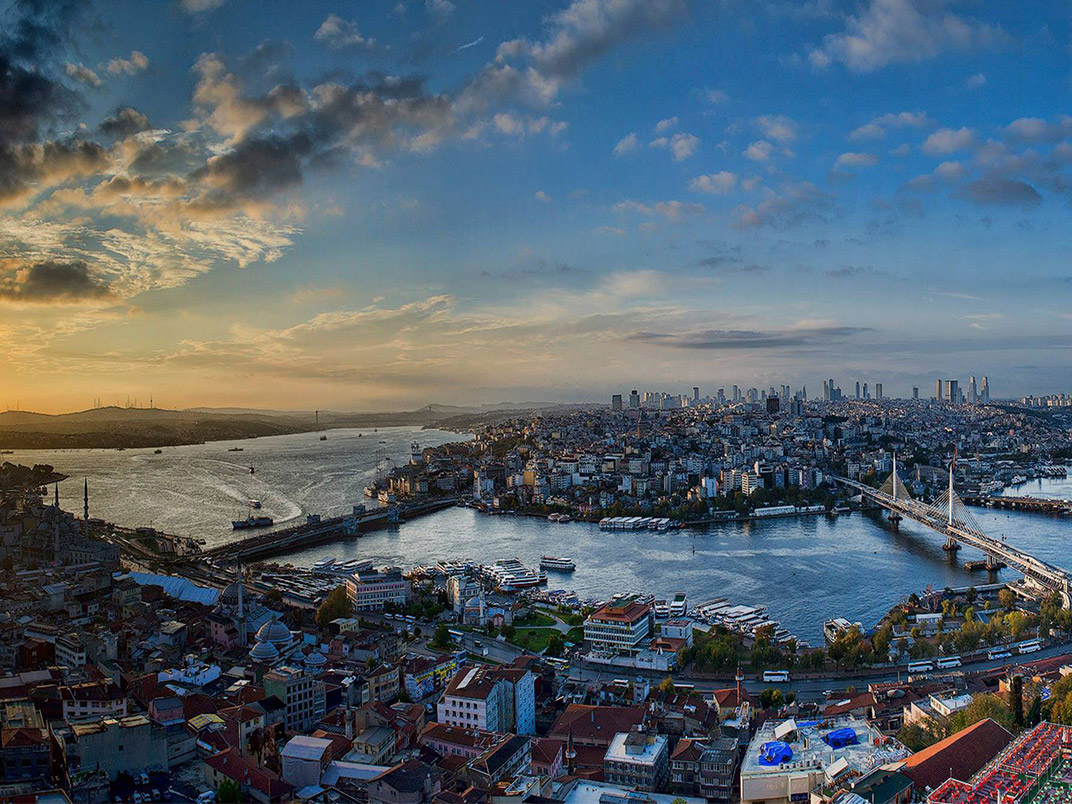

4. Natural Beauties
Turkey, which experiences four seasons, has a reputation for its natural beauties all over the world. You can enjoy swimming and water sports in the seas that surround Turkey, you can ski in many cities in the mountains, you can enjoy rafting in the rivers and experience many extreme sports. You will feel as in the heaven in Turkey where countless beauties which shall only fascinate you with their landscape!
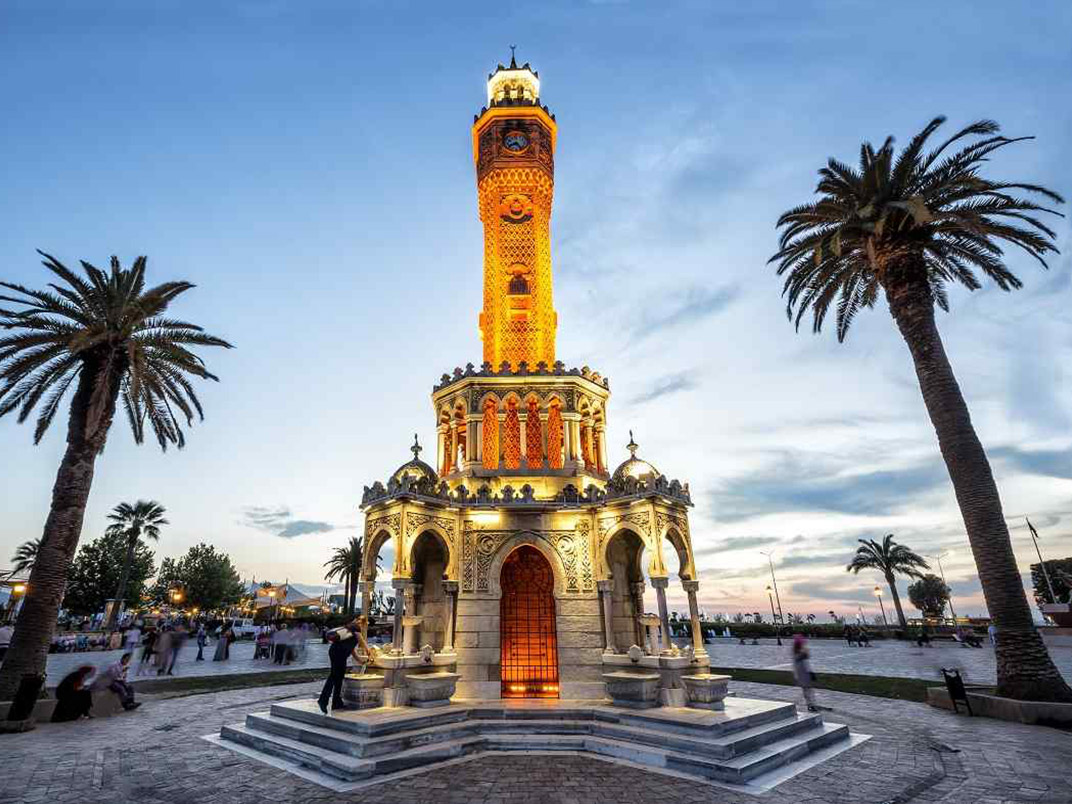
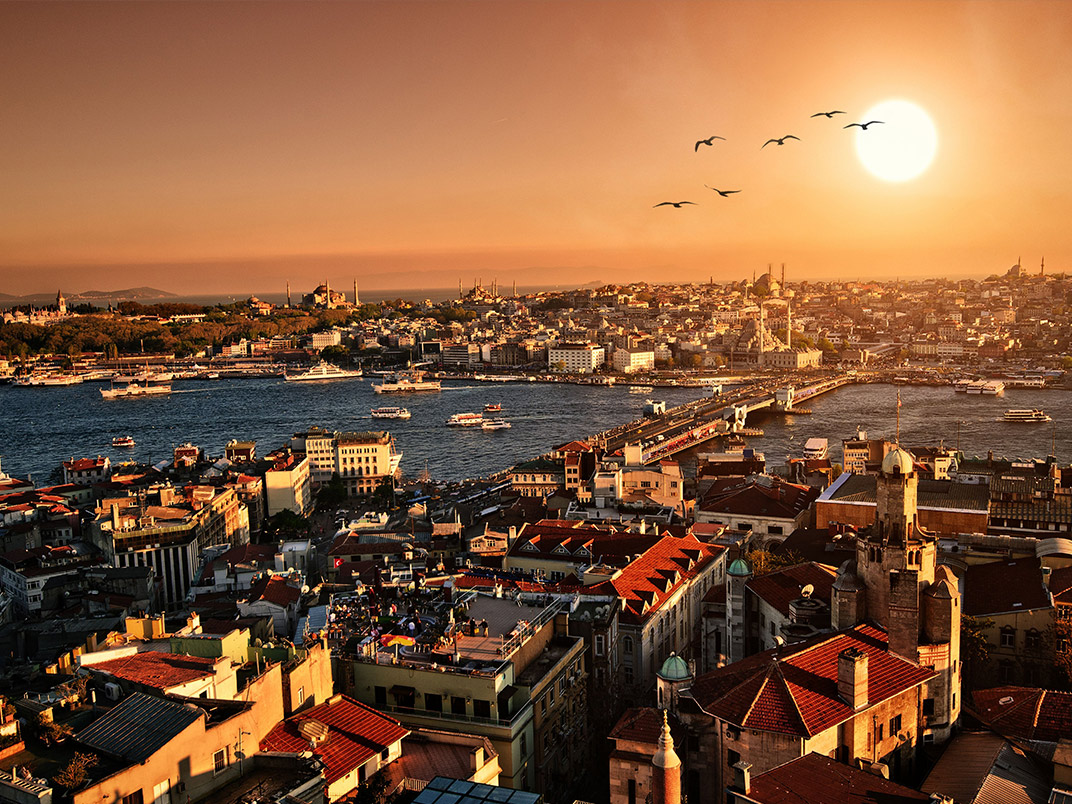



5. Historical and Cultural Heritage
Based on a long history, there are thousands of historical and cultural monuments in Turkey, many of which are protected as UNESCO Cultural Heritage. Even in your daily life, you will want to keep track of the traces you may encounter frequently!
6. Student Friendly
With at least one university in every city, Turkey is exactly a student-friendly country! Social clubs, sports teams and cultural events at every university bring together students and make distant geographies close. When you arrive in Turkey you will understand that the most active points of the city are the places where students socialize! Thanks to the cafes, restaurants and libraries where the students hang out, the cities live 24 hours a day.

7. Hospitable Turkish People
The hospitality of Turkish people has been legendary all over the world! As a student, if you ask for help, people will do their utmost with all sincerity and friendliness. Turks will welcome you as guests and have many treats to satisfy you. Be sure you won’t be miss your home here!

8. Modern Technological Campuses
No matter which one of the 206 universities you go, you will experience a modern and convenient campus life, equipped with the latest technology.

9. Easy Living Conditions
Life in Turkey is more affordable than most countries. You can meet your needs, such as accommodation, food and drink, and entertainment at affordable prices. You can stay at the dormitories within or near the University campuses, or rent a house for a reasonable lease. In addition, whichever transportation you choose as a student, you will receive a ticket at a discounted price, or watch the movie in the cinema at cheaper.
Turkey is also an easy to reach country because it is in the middle Asia and Europe continents. Whichever way you choose to discover Turkey, which hosts countless places of attraction, you can arrive where you want quickly and comfortably.
10. Turkish Learning Opportunities
Several programs in Universities in Turkey are in English. Besides you can also learn Turkish, the 5th most spoken language in the world! You can get a chance to learn a new language in Turkish courses that your University will offer you, and you can be friends with people from many different cultures.
Turkish Higher Education System
General Structure
In 1981, in accordance with the new Higher Education Law (No. 2547), the administration of higher education in Turkey was comprehensively restructured. The system thereby became centralized, with all higher education institutions tied to the Council of Higher Education (CoHE). After this restructuring, all institutions of higher education were designed as universities. Expansion of higher education throughout the country was achieved, application to higher education was centralized, and a central university exam and placement were introduced. In addition to public universities, the first nonprofit foundation university in Turkey started to provide education for students in 1986.
Since 2012, compulsory education in Turkey lasts 12 years and is divided in three stages (primary education, elemantary education and secondary education).
Pre-primary School Education: It involves the education of children in the age group of 3 to 5 who have not reached the age of compulsory primary education, on an optional basis.
Primary Education: It involves the education and training of children in the age group of 6 to 10. Primary education is compulsory for all citizens. It is free at the State schools and lasts four years (1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th grades).
Elemantary Education: It involves the education and training of children in the age group of 10 to 14. Elemantary education is compulsory for all citizens. It is free at the State schools and lasts four years (5th, 6th, 7nd, 8th grades). Towards the end of the elemantary school, pupils are given information about both general, vocational and technical high schools and the kinds of employment they prepare for.
Secondary Education: It comprises high schools of a general or vocational and/or technical character giving four-year courses aiming children at the age of 14 to 17 (9th, 10th, 11th, 12th grades). Secondary education is compulsory for all citizens and is free at the State schools.
Higher Education: After graduating from high school, students can enroll in higher education, which is compatible with the Bologna three-cycle system.
Types Of Higher Education Institutions And Academic Units
Faculty (College): A division conducting higher education, scholarly research and publication. Various departments and programmes may be connected to it. Students earn a Bachelor’s degree at the end of an educational programme that lasts for at least four years.
Graduate School: An institution in universities concerned with graduate education, scholarly research and applications. Graduate schools award MA, MSc or PhD degrees.
4-year School: An institution of higher education which is mainly concerned with providing instruction for a specific profession. It lasts for eight semesters.
Conservatory: An institution of higher education in which artists are trained for music and the performing arts. It lasts for eight semesters.
Post-Secondary Vocational School: An institution of higher education that is aimed at training human capacity in specific professions and provides instruction lasting four semesters.
Research and Application Center: An institution of higher education carrying out research and applied studies to meet the applied study needs of various areas and to provide preparatory and support activities for various professional areas, with the aim of supporting education in institutions of higher education.
Degrees
Associate’s degree (short cycle): Awarded on completion of a two-year study program. The associate degree programs are offered by universities and foundation postsecondary vocational schools. Some distance education programs are also available. The associate degree programs may require a period of on-the-job training.
Bachelor’s degree (1st cycle): Awarded after the completion of a four-year course and 240 ECTS of study. The duration of study for dentistry, veterinary medicine and pharmacy is five years and that of medicine is six years. The qualifications in these four fields are considered to be the equivalent of a Master’s degree.
Master’s degree program (2nd cycle):Two-year program leading to the Master of Arts (MA) or Master of Sciences (MS). There are two kinds of Master’s programs, with or without a thesis. The Master’s with thesis program is a two-year program generally consisting courses with a minimum of 120 ECTS followed by submission of a thesis. Non-thesis programs are to be completed in one or one and a half years and call for the completion of graduate courses of a minimum 90 credits and a term project.
Doctoral degree program (3rd cycle): Usually an eight-semester program leading to the PhD degree. It consists of courses, with 180-240 ECTS, a proficiency exam, a dissertation proposal, a dissertation and its oral defense. After successful completion of the course work and the proficiency exam, students must submit the dissertation and defend it orally before an examining committee.
Specialization in Medicine Programs: They are equivalent to doctoral degree programs and are carried out in the faculties of medicine, university hospitals and research and training hospitals. For the specialization in medicine, there is a competitive selection examination in various branches of medicine for those graduating from the faculties of medicine. Specialist candidates are required to submit a dissertation and defend it before an examining committee.
Proficiency in Art: It is at least a six-semester post-Master’s program in the visual and performing art branches making it equivalent to a Doctorate. It requires the presentation of an original work of art or (in music and the performing arts) a superior, creative performance.
International Student Admissions
International students who wish to undertake their undergraduate studies in Turkey must have completed their secondary education in a high school or similar institution in which the education is equivalent to that of a Turkish high school. They apply directly to the university of their choice and the university makes the selection.
international students who wish to pursue their graduate / post-graduate studies in Turkey also apply directly to the universities, which set their own admissions requirements. There are also various scholarship options which are available for some international students.
Tuition Fees
Tuition fees are applied differently in public and non-profit foundation universities. In public universities, tuition fees are decided and announced by the Council of Ministers, taking into consideration the type and duration of study in different disciplines. In non-profit foundation universities, on the other hand, tuition fees are decided by the Board of Trustees of the university.
Students must pay their tuition fees for each semester before registering for the courses at the beginning of that specific semester. Both in public and non-profit foundation universities, a certain percentage of the students are admitted to the university are given diverse scholarships. These scholarships may be ful lor partial tuition waiver, merit or support scholarships. Some of these scholarships may meet academic materials, accommodation, food and beverages, and even certain allowances. In addition to this support, student assistantship and the research fellowships are another kind of support that could be helpful during the study in Turkey.
Message from the President
Prof. Dr. M. A. Yekta Saraç President of Council of Higher Education
 Territory of Republic of Turkey which witnessed various civilizations throughout history, and carries a unique cultural heritage has been enriched by achievements from both the Eastern world and the Western world. Tradition of higher education, which is one of the reflections of this history, dates back to the XVth century, until foundation of most important educational institution of the period “Sahn-ı Seman”, which is known as Istanbul University today.
Territory of Republic of Turkey which witnessed various civilizations throughout history, and carries a unique cultural heritage has been enriched by achievements from both the Eastern world and the Western world. Tradition of higher education, which is one of the reflections of this history, dates back to the XVth century, until foundation of most important educational institution of the period “Sahn-ı Seman”, which is known as Istanbul University today.
Higher education area of Turkey, with quantitative growth it has demonstrated in recent years, has made significant progress in many areas, especially in access to higher education. As of Today, more than 8 million students, 206 higher education institutions with over 160 thousand lecturers constitute the higher education area of Turkey. Turkey is the most prominent country in the European Higher Education in terms of the number of students. In addition to this quantitative size, policies are determined to enable our institutions to perform their own missions in a higher quality manner, decisions are taken within the framework of regional development-oriented mission differentiation, research universities are selected and investments are being made accordingly. As a result, our higher education institutions come to better points in their fields, integrate with their regions and become the focus of attention in their regions.
Access to higher education, internationalization and quality of higher education are the fundamental issues related to higher education area. Within the framework of our country’s Vision 2023 goals, our main objectives are to produce policies that will that facilitate access to higher education and increase the qualified human resources, to further improve our mission differentiation and specialization project and to develop various strategies in order to make Turkish Universities, an international center of attraction. When we look at these main objectives, we can say that we are at a very satisfactory point of access to higher education. In fact, according to The World Economic Forum’s “2017-2018 Global Competitiveness Report”, Turkey is ranked second among 137 countries in the title of Access to Higher education.
The second important issue after quantitative, numerical achievements obtained by access to higher education is to raise the quality bar in higher education. For this purpose, administrative and financially independent Higher Education Quality Council was established in 2015. Today, each of the universities under the higher education system in Turkey are obliged to pass at least once in five years from institutional external evaluation process carried out by Higher Education Quality Council, which gained autonomy in 2017. Increasing threshold score in Higher Education admission system, introducing limitation in the order of success in Medicine, Law, Engineering, Architecture and Teaching Programs approved by all sections of the society and initiating base score application, increasing admission criteria of doctorate, initiation of accredited programs in guideline where associate and graduate degree programs are listed, updating of teaching principles of foreign language education are some of the many important projects developed to increase input quality of Higher Education System.
As Presidency of Council of Higher Education, we believe that internationalization in higher education is an investment for the future and that it should progress as a as a sustainable process with an understanding of responsibility towards students, academic staff and institutional stakeholders.
In the last few years, significant increases have been observed in the number of international students involved in the Turkish Higher Education System. The number of international students, which was 48 thousand four years ago, exceeded 148 thousand today. International students who prefer to study in Turkey are faced with European standards of education opportunities in various fields. On the other hand, among the countries that have European Credit Transfer and Spool System Label (ECTS Label), in terms of the number of universities receiving the ECTS label, Turkey has always been ranked first among AYA/European Higher Education Area countries since 2009. The number of universities that have Diploma Supplement Label (DS Label) is 73. The diplomas that our students will eventually obtain are not only recognized throughout Europe, but also an important key that opens the door to them in many leading countries of the world.
With the inclusion of Turkey in the Bologna Process in 2001, the academic recognition, which is another important element of internationalization, has been placed in a more priority position in Turkish higher education. More than 45 thousand students, who are offered internationally qualified education in over associate’s, undergraduate, master’s and PhD degrees, 2748 of which are provided in foreign languages have a chance to continue their education in a foreign country. Through the Erasmus/Erasmus + program, more than 55 thousand students have come to our country for education since 2004, and around 150 thousands of students have gone to different countries of European Union and continued their educations abroad for one or two semesters. At the Ministerial Summit of the European Higher Education Area, which was held between 24-25 May 2018, Turkey has taken 5 over 5 full points and has once again demonstrated that it is in front of many European countries in terms of the achievements defined by the Bologna Process under “Qualifications Framework”, “European Credit Transfer System” and “Diploma Supplement” subjects of Development of Degree Systems main topic.
Mevlana Exchange Program, which is initiated and supported by the Council of Higher Education, is a student and academician exchange program of Turkish universities and universities abroad, which allows students to study at a university abroad for a period of one or two semesters. Within the framework of this program, the number of Mevlana Exchange Protocols signed between our universities and universities abroad has reached 2.860.
Project-Based International Exchange Program is another important step that CoHE has taken towards internationalization of higher education. Higher education institutions develop joint projects in areas approved by Executive Council of Higher Education. Within the scope of this program, support has been provided for the exchange of students and academic staff to 93 joint scientific projects conducted between our universities and 36 universities of other countries.
Education and training quality of Turkish Higher Education System is increasing day by day. “Mobility” and “Exchange” opportunities that we offer to our students and academicians, as well as joint projects and joint diploma programs conducted with reputable universities of the world contribute this. Today, the number of joint diploma programs with major universities in the world, especially in the UK, France and Germany universities, has reached 226.
We have been implementing CoHE International Scholarship Program with success for three years to meet the needs of the trained manpower of some close countries. The basic feature of this program, which is unique in the world, covers determination of the areas to be studied by the relevant country. After graduation, those scholars are obliged to perform their compulsory services in their own countries. In this respect, CoHE foreign scholarships are prioritized for the benefit of his/her country rather than the benefit of the individual. Thus, Our Council of Higher Education offers a significant contribution to the efforts of New Turkey in the understanding of sharing its possibilities with friendly and sibling countries.
I invite International students to study in Turkish universities where quality and qualified education is offered in many areas, especially in health and engineering areas. I strongly recommend that they do not miss the opportunity to reach their dreams with diplomas they will achieve in Universities of Turkey by experiencing the privilege of great hospitality of Turkish people, who cherish Eastern and Western civilizations and cultures live together and who see diversity and differentiation as wealth.